- Raising InvestorIQ Newsletter
- Posts
- Return on Equity Analysis
Return on Equity Analysis
RIIQ Key Investing Insight
DISCLOSURE: THIS POST MAY CONTAIN AFFILIATE LINKS, MEANING I GET A COMMISSION IF YOU DECIDE TO MAKE A PURCHASE THROUGH MY LINKS, AT NO COST TO YOU. PLEASE READ MY DISCLOSURE FOR MORE INFO.


A Key Profitability Indicator
Effectively Evaluate a Company’s Profitability With This Analysis
Good morning investors!
If this is your first time reading, welcome to Raising InvestorIQ!
Every Sunday morning, we publish a free write-up within our RIIQ Newsletter with leading insight and analysis — the aim is to help investors of all skill levels focus on key fundamentals, gain confidence in developing an investment strategy, and gain an edge in the push to generate true wealth.
Grab your coffee and let’s dive in!
Deep-Dive
Intro
Let’s say you’re browsing through some stocks, trying to figure out which one is worth your hard-earned cash. You’ve read up on the companies, checked their growth stories, and even considered their future prospects. But how do you know if they’re really using their money (their capital) efficiently?
That’s where Return on Equity (ROE) comes into play—a key financial metric that helps you see if a company is making smart decisions with its shareholders' money. Think of ROE as a window into a company’s ability to turn investment into profit.
Curious? Let’s break it down and see why this one ratio can give you major insights into whether a stock deserves a spot in your portfolio.
What’s ROE and Why Should You Care?
Think of ROE as the "bang for your buck" indicator. It measures how effectively a company is using its shareholders’ money to generate profits. Here’s how it works in simple terms:
ROE = Net Income / Shareholders’ Equity
So, what does that mean?
Net income is the company’s profit after expenses, and shareholders' equity is the total value that’s been invested in the company by its owners. The higher the ROE, the better the company is at turning every dollar invested into actual profit.
Now, why should you care? Because ROE gives you a peek behind the curtain. It helps you see whether a company is growing efficiently or just spinning its wheels. And while it’s a great standalone metric, it’s even more powerful when you compare it to the same metric of other companies in the same industry.
Analyzing this metric is key to identifying solid investment prospects and weeding out those that aren’t worthwhile. Let’s dig in deeper…
Calculating ROE Without Losing Your Mind
Calculating ROE is actually as simple as it gets in the world of finance. You take the company’s net income (found on its income statement) and divide it by the shareholders' equity (found on its balance sheet). Here’s a quick example to bring it home:
Let’s say Company XYZ reports a net income of $5 million, and its shareholders' equity totals $25 million. The ROE would be:

That means Company XYZ is generating 20 cents of profit for every dollar of shareholder equity. Nice and simple, right?
But remember, as is always the case with these type of indicators, context is key. The number alone doesn’t mean much without comparing it to others in the same sector. A 20% ROE in one industry might be stellar, while in another, it could be pretty standard.
ROE: Not Just a Number—A Story
Numbers can tell a story, and ROE is no exception. A company’s ROE reveals how well it’s managing its resources and whether it’s worth your investment. But what exactly is a “good” ROE?
For many investors, a ROE above 10% is considered a decent benchmark, though that varies by industry. In capital-intensive sectors, like utilities, lower ROEs are more common. In tech or retail, where assets tend to be lighter, a higher ROE is often expected.
Take the S&P 500 as a point of reference. The average ROE for companies listed there is around 21.7% as of mid-2024. If a company’s ROE is significantly higher, it might be a sign that they’re doing something right—or that there’s something you need to investigate further.
When ROE Turns Sour: AT&T vs Apple
Let’s put theory into practice with two well-known companies: Apple and AT&T. Both are giants in their respective industries, but their ROEs tell very different stories.
Apple: A Masterclass in High ROE

Apple ROE trajectory
Apple consistently posts a strong ROE, and as of 2024, it sits at a healthy 160%. So, what’s behind this number?
For one, Apple knows how to manage its equity efficiently. It has high profit margins on products that dominate the market, meaning they don’t need to plow huge amounts of cash into assets to generate profits. Apple’s sleek product line and brand loyalty translate into robust revenues with relatively low costs, boosting both profits and ROE.
Another factor behind Apple’s impressive ROE is its savvy use of debt. Apple does borrow money, but it’s smart about it. With a debt-to-equity ratio around 1.51 (see graph below), Apple uses this borrowed cash to fund profitable ventures that generate returns far greater than the cost of the debt. That’s the kind of leverage you want to see.
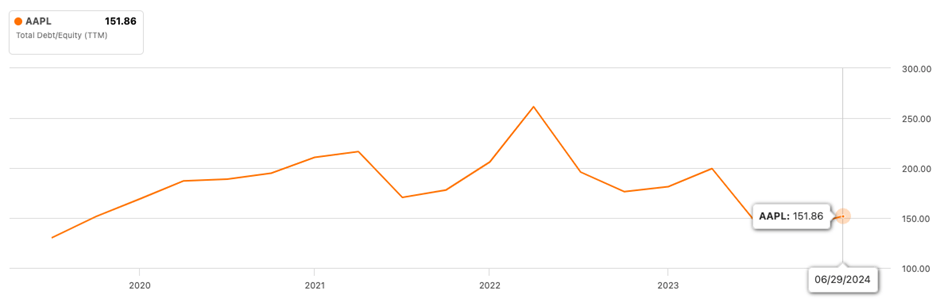
Apple’s debt-to-equity (D/E) ratio trajectory
This high ROE shows that Apple is a well-oiled machine, effectively using both shareholders’ investments and borrowed funds to keep growing.
AT&T: When ROE Drops the Ball
On the flip side, AT&T has struggled with a low ROE, often hovering around the 10% mark or lower. While 10% might not seem terrible on the surface, for a company of AT&T’s size and industry, it raises some concerns.

AT&T ROE trajectory
On the flip side, AT&T has struggled with a low ROE, often hovering around the 10% mark or lower. While 10% might not seem terrible on the surface, for a company of AT&T’s size and industry, it raises some concerns.
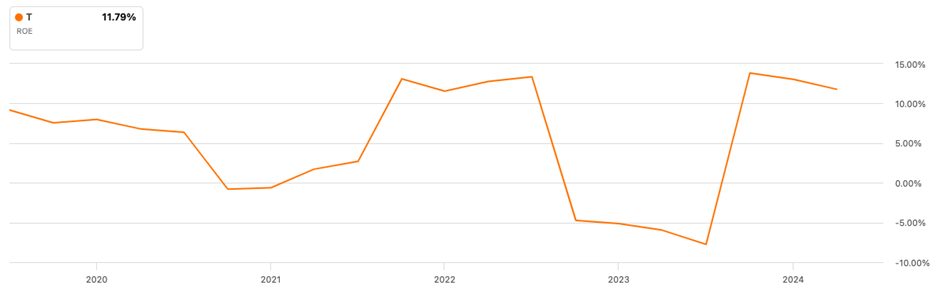
AT&T Return on Equity (ROE) trajectory
What’s going wrong here? A big part of AT&T’s issue is its massive debt load. Over the years, AT&T has made several large acquisitions, like the costly buyout of Time Warner.
While acquisitions can sometimes boost growth, they’ve saddled AT&T with significant debt. Since ROE is calculated by dividing profits by equity (which is assets minus liabilities), high levels of debt reduce the equity figure, pushing down ROE.
Another problem is that AT&T operates in a mature, highly competitive industry—telecommunications. Unlike tech giants like Apple, where margins are high, AT&T’s margins are squeezed by competitors and massive infrastructure costs. The end results? Less profit and a lower return on equity.
So, while Apple’s high ROE signals effective management and growth, AT&T’s lower ROE suggests struggles with profitability and an over-reliance on debt. This contrast helps illustrate why ROE isn’t just a number—it’s a glimpse into a company’s entire strategy.
The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly of ROE
Now that we’ve seen both ends of the ROE spectrum, let’s get a bit more specific about what makes a good or bad ROE.

The Good
A high ROE, like Apple’s, typically indicates that a company is making efficient use of its equity to generate profits. This could mean they have strong profit margins, a competitive advantage, or simply better management. High ROE companies are often more appealing to investors because they can deliver returns without needing a ton of new investments or debt.
But remember, a super-high ROE isn’t always sunshine and rainbows. It’s important to check whether the ROE is sustainable. If it’s inflated due to excessive borrowing, as with some companies, that could spell trouble down the line.
The Bad
A low ROE, on the other hand, signals potential issues. If a company’s ROE is consistently underperforming relative to its peers, it might be struggling to use its resources efficiently. For instance, AT&T’s ROE isn’t just lower than the tech giants—it’s also underperforming compared to other companies in the telecommunications sector.
This suggests internal issues, like poor capital management or slow growth prospects. Low ROE can also be a red flag if a company is stuck in a cycle of borrowing heavily to stay afloat. Remember, ROE doesn’t take debt into account directly, so a company could have an artificially low ROE simply because it’s overwhelmed by debt.
The Ugly
And then there’s the worst-case scenario: negative ROE. This happens when a company is losing money, meaning its net income is negative. In this case, shareholders are effectively losing value.
While negative ROE might be expected in startups or companies going through heavy growth investments, it’s generally a red flag for more established businesses.
The ROE Sweetspot: How to Use It Wisely
As with any financial metric, the magic happens when you know how to use ROE properly. Here are a few tips to get the most out of it:
Compare within industries: Always compare a company’s ROE to others in the same sector. What’s considered a good ROE in tech might be different from what’s acceptable in energy or utilities (see graph below with the contrast with companies like Dell and HP with negative ROE, indicating that they are losing money or have excessive debt compared to their equity).

Look at trends: Don’t just focus on the current ROE—look at how it has evolved over time. A rising ROE is usually a positive sign, while a declining one might warrant further investigation.
Check for debt: High debt levels can artificially inflate ROE, so always check the company’s debt-to-equity ratio to see if it’s taking on too much risk.
Combine with other metrics: ROE is great, but it’s just one piece of the puzzle. Pair it with metrics like Return on Assets (ROA) and Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) to get a fuller picture of the company’s efficiency.
Final Thoughts: ROE is Just the Beginning—Keep Learning

ROE is undoubtedly a powerful tool for any investor, offering a solid snapshot of how well a company uses its money to generate profits. But here’s the thing: ROE is just one piece of the investment puzzle.
To truly master the game, you need to understand how different metrics work together. You can’t rely on ROE alone to make investment decisions. For instance, how does a company’s debt impact its overall financial health? What about its cash flow?
That’s why it’s crucial to keep exploring and learning about other financial indicators, as they are all interconnected. ROE might give you the headline, but other metrics like ROA, ROIC, and debt ratios provide the context.
So, stick with Raising InvestorIQ, and keep reading these newsletters—because mastering one ratio is great, but understanding how they all fit together is what will give you that winning edge in the market!
Key Insight
A super-high ROE isn’t always sunshine and rainbows. It’s important to check whether the ROE is sustainable. If it’s inflated due to excessive borrowing, as with some companies, that could spell trouble down the line.
Visit and subscribe for FREE to the Raising InvestorIQ YouTube Channel for more leading Investing info, insight, and analysis.
Disclosure/Disclaimer
As a Tykr affiliate, Raising InvestorIQ earns from qualifying purchases. As a Seeking Alpha affiliate, Raising InvestorIQ earns from qualifying purchases.
Information provided on this site is based on my own personal experience, research, and analysis, and it is not to be construed as professional advice. Please conduct your own research before making any investment decisions. I am not a professional financial advisor, stockbroker, or planner, nor am I a CPA or a CFP.
The contents of this site and the resources provided are for informational and entertainment purposes only and do not constitute financial, accounting, or legal advice. The author is not liable for any losses or damages related to actions or failure to act related to the content on this website.


